Anu-Ujin Gerelt-Od

NYU M.S. Data Science, 2021
USF B.S. Quantitative Economics & Econometrics, 2018
LinkedIn Profile
Portfolio
Index
- Analysis of Indirect Question Answering Models Using Transfer Learning Techniques
- Generating Feature Impact from Individual Conditional Expectation Plots
- One Medical Passport: Predictive Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Neural Machine Translation: Vietnamese-English
- Keepin’ It Real: How to Identify Fake and Genuine Reviews
- Python Price Tracking and Monitoring Tool
- Goodreads Book Recommender System
- Food Happens in Vegas: How Can Restaurants Improve Their Yelp Profiles for Success?
- Amazon.com and Its Effect on the Retail Market and Employment
Projects
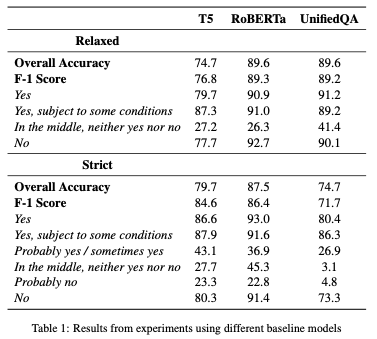
Analysis of Indirect Question Answering Models Using Transfer Learning Techniques
Abstract
The IndirectQA task aims to understand responses to naturally occurring boolean questions which do not contain direct cue words. Building models that perform well on this task can be instrumental in improving performance of conversational chatbots, as well as interactions with robots or other AI agents. In this paper, we explore the recently developed Circa dataset of indirect question-answer pairs, attempting to replicate and then improve upon its classification results. We first implement the same BERT-based models fine-tuned on other datasets reported in the original paper, and then run similar experiments on other model architectures using T5, RoBERTa, and UnifiedQA. The RoBERTa model fine-tuned on MNLI and Circa achieved the highest accuracy on the test set, in both the strict (87.5%) and relaxed settings (89.6%), as well as the highest F-1 scores on both the strict (86.4%) and relaxed (89.3%) settings.
Results from experiments using different baseline models
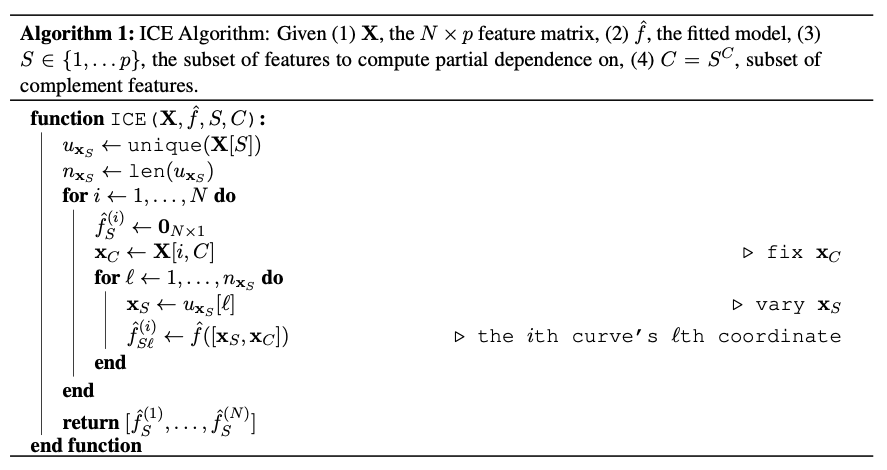
Generating Feature Impact from Individual Conditional Expectation Plots
Abstract
As machine learning systems become ubiquitous, methods for understanding and interpreting these models are increasingly important. In particular, practioners are often interested in both what features the model relies on and how the model relies on them – the feature’s impact on model predictions. Previous work on feature impact including partial derivative plots and individual conditional expectation (ICE) plots has focused on a visual interpretation of feature impact. To address shortcomings in ICE, we propose several modifications for visual clarity and computational efficiency. To quantify feature impact, we also introduce ICE feature impact, a model-agnostic, performance-agnostic feature impact metric extracted from ICE plots. Additionally, we introduce an in-distribution variant of ICE feature impact to reduce the influence of out-of-distribution points. To assess utility, we conduct an experiment comparing ICE feature impact with random forest feature importance scores in a real-world dataset.
Proposed change to the ICE algorithm
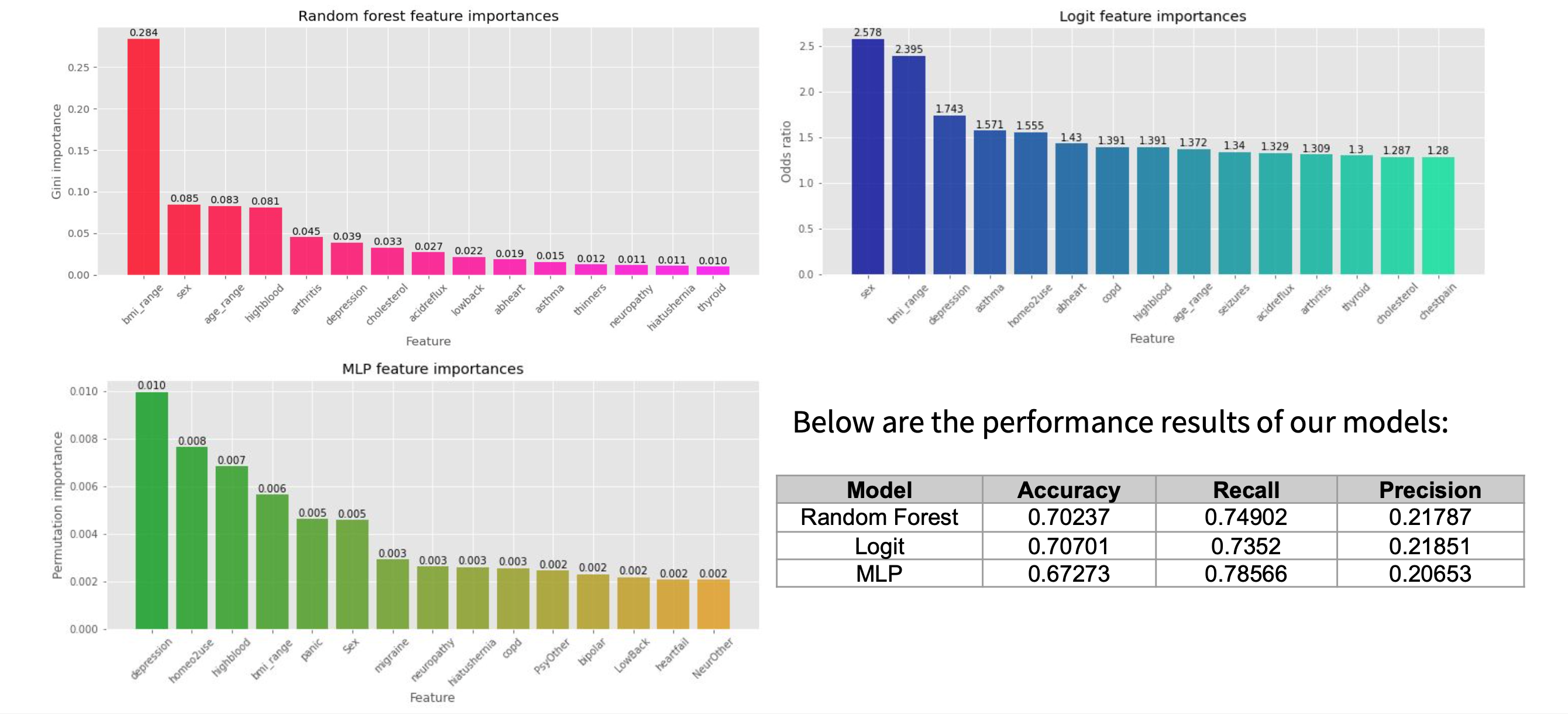
One Medical Passport: Predictive Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
The use of machine learning algorithms in the medical field has gained traction on account of its ability to provide more concrete and accurate results. This research was conducted in cooperation with the healthcare SaaS company One Medical Passport to examine potential predictors of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and to create a pre-screening tool. We used various machine learning and deep learning algorithms including logistic regression, random forest, multi-layer perceptron, and K-modes clustering to assess the predictive power of 4 out of the 8 criteria included in STOP-BANG which is the most widely-used OSA screening questionnaire, and also explored other possible predictors that could be used to augment the existing questionnaire.
Top 15 features and their importance weights, according to our models
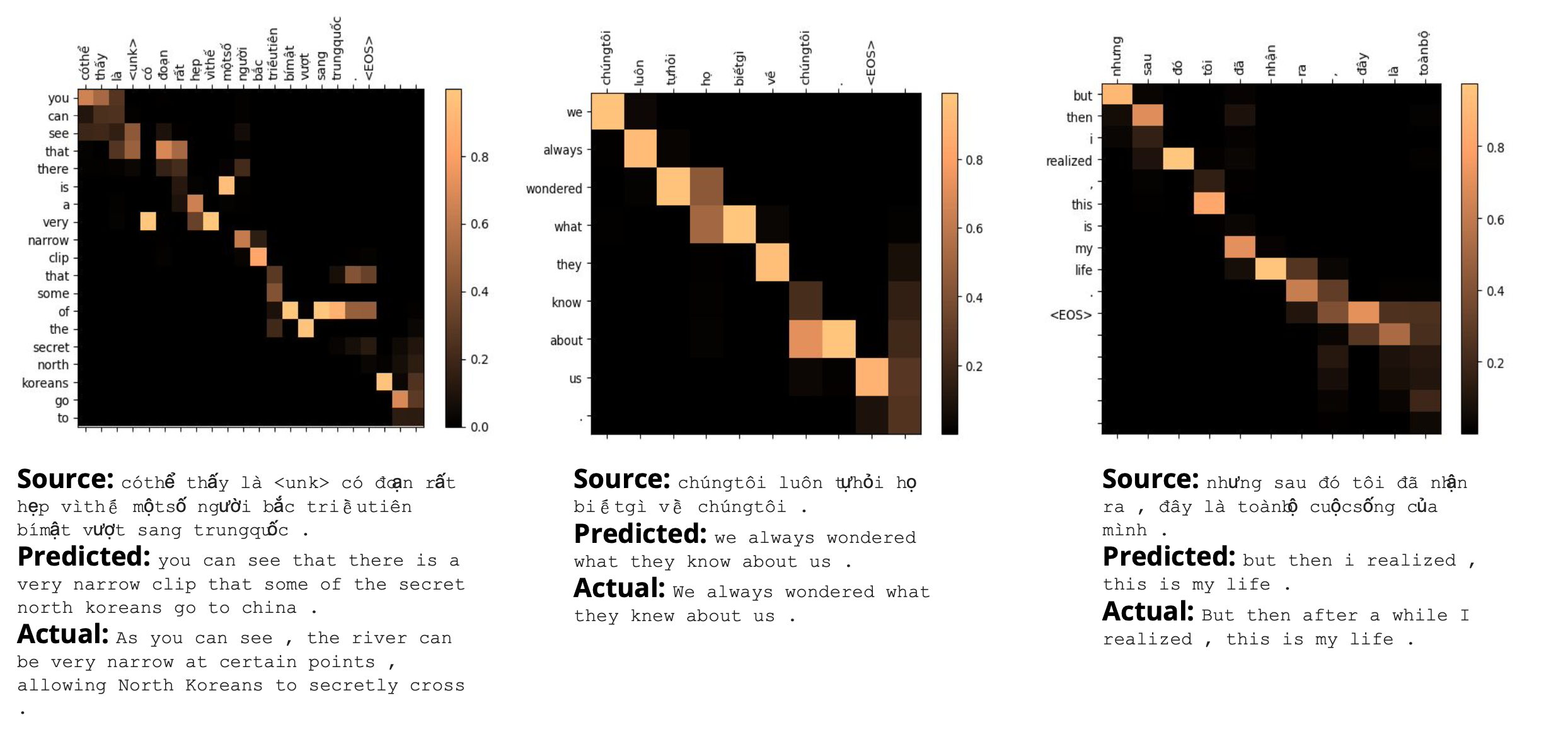
Neural Machine Translation: Vietnamese-English
Abstract
The performance of NMT models are highly sensitive to the amount of available training data. For this reason, low resource language pairs such as English- Vietnamese often suffer from poor performance. In the scope of this project, the IWSLT’15 English-Vietnamese dataset was used to experiment with different encoder-decoder architectures using LSTM and GRU RNNs, and hyperparameter tuning to maximize NMT model performance.
Sample translations showing from left to right: complications with <UNK> tokens, grammatical errors, and a good translation
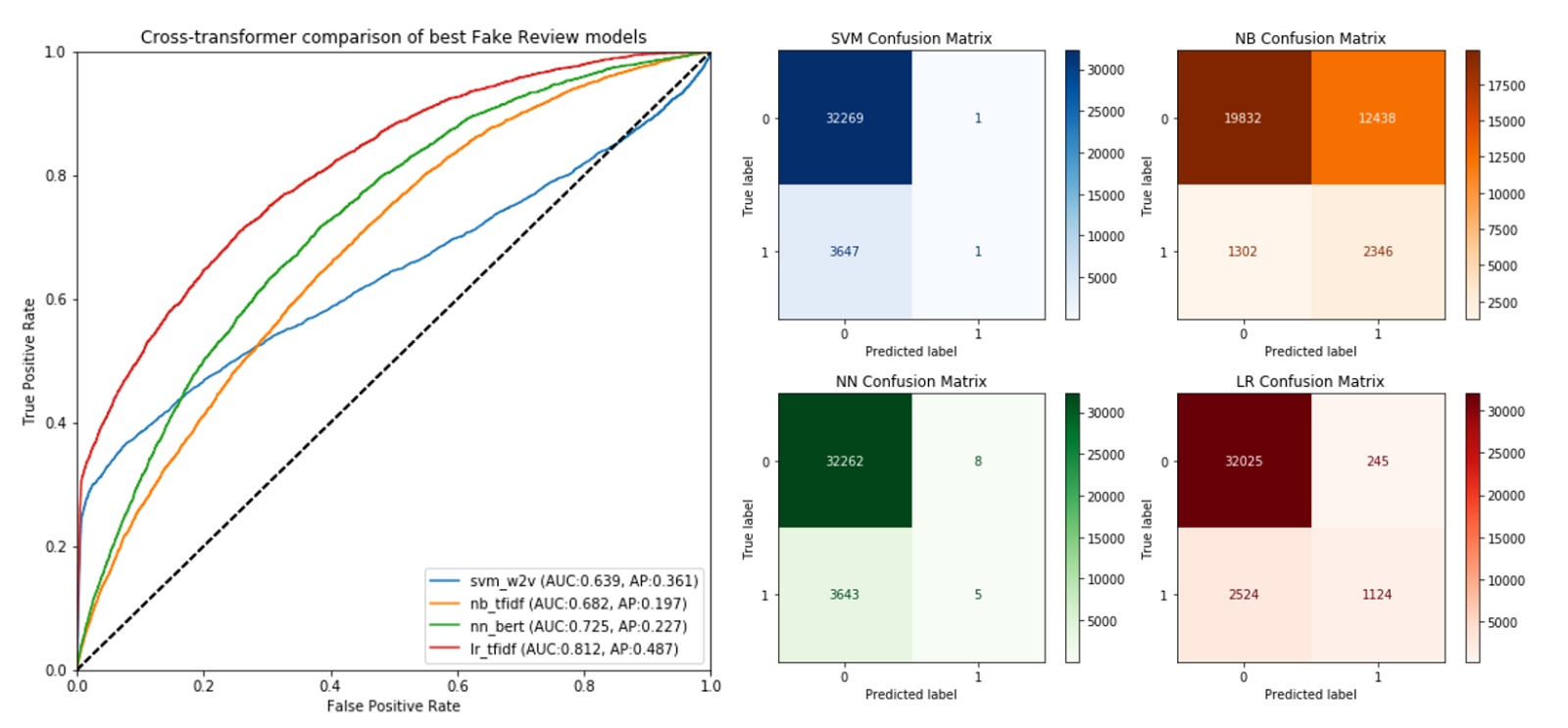
Keepin’ It Real: How to Identify Fake and Genuine Reviews
Abstract
Reviews have quickly become an important decision making tool for consumers considering both online and offline spending. Thus, for a new industry around buying and selling Fake Reviews has risen to meet the demand of unscrupulous businesses. The goal of this project is to generate a model that successfully classifies Fake and Genuine reviews.
Visualization of the models’ performance and precision scores
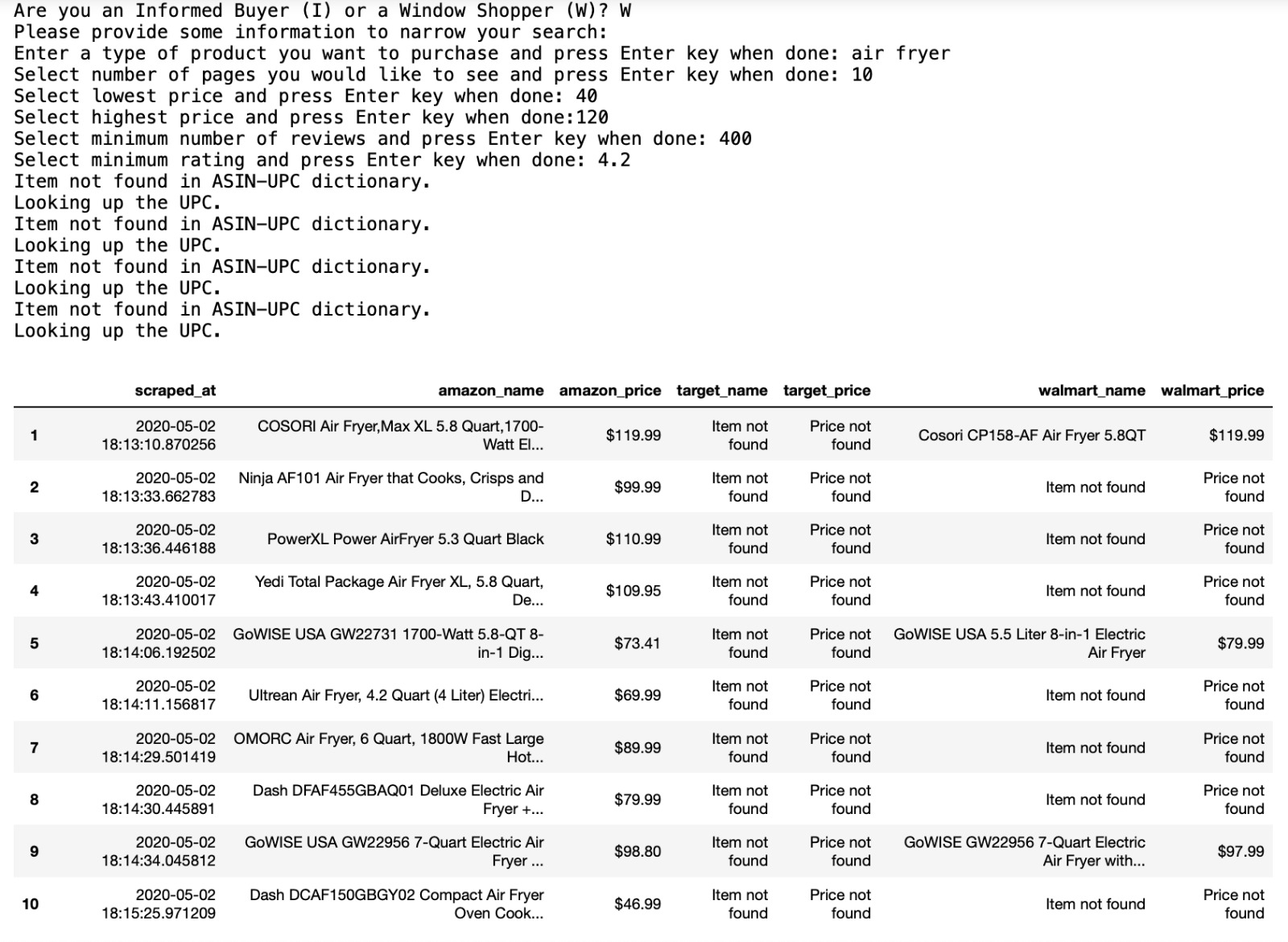
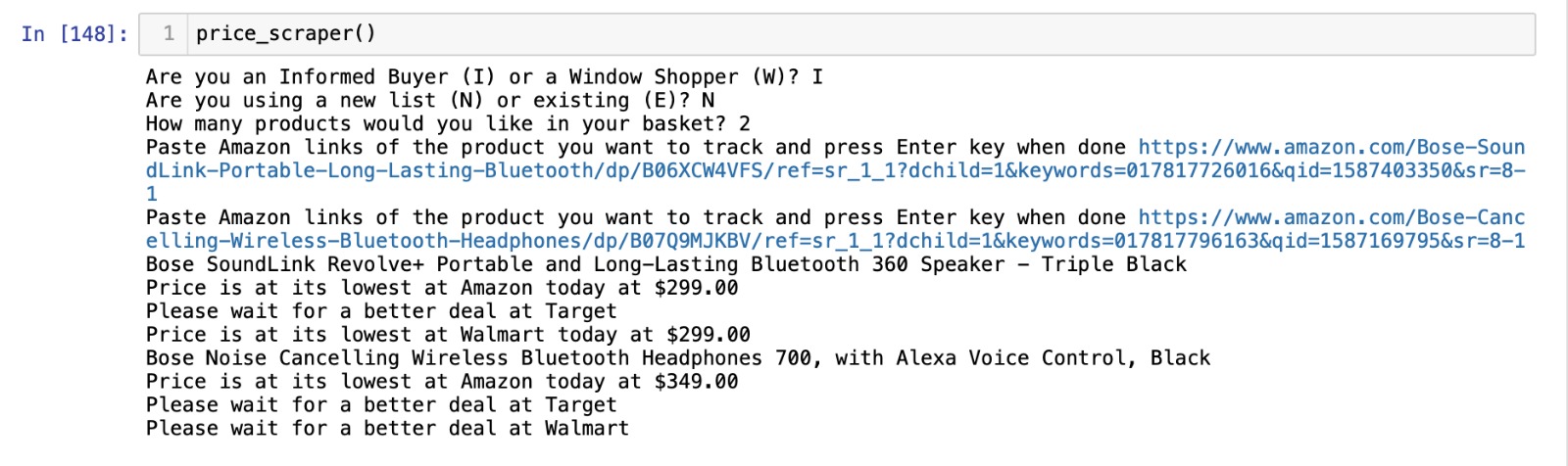
Python Price Tracking and Monitoring Tool
Abstract
It has become increasingly difficult to shop as a rational consumer and buy products from retailers offering the lowest prices. There are differences in prices in the market; retailers offer the same product for different prices and external factors create price fluctuations over time. In our project we tracked prices across three major e-commerce companies: Amazon, Target and Walmart. We enable users to track baskets of items over time by providing specific URLs of items from Amazon or search for products using a keyword. Users can explore price data and check how prices change over time or which retailer sells a given item for the cheapest price at a given time by exploring graph of the prices.
Sample run of the price comparison tool for a Window Shopper
Sample run of the price scraper for an Informed Buyer
Example of the price tracker for an Informed Buyer
![]()
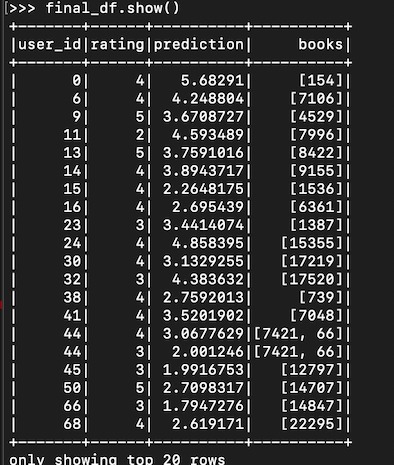
Goodreads Book Recommender System
Abstract
Recommender systems are a driving force for a variety of businesses such as retailers and entertainment services, and their popularity is only rising. On the business side, it allows the companies to offer a wide range of products, without limiting them to a confined physical space. As for the users, it makes it easier for them to make a decision when consuming a product by giving them a personal recommendation based on the choices made by users with similar interests. This project explores a basic recommendation system implementation, with a comparison to single machine implementations extension. The data set that is used for this project was provided by Goodreads - an online platform for readers to share their opinions on books they’ve read. As we have explicit feedback from the users in the form of a rating, we have used a Collaborative Filtering approach, which creates a recommendation based on the behavior history of the user as well as of users that have similar interests. Additionally, as the data matrix for this type of problem is usually very sparse, we have used an Alternating Least Squares method to process the data set and make predictions.
Sample output from the Recommender System
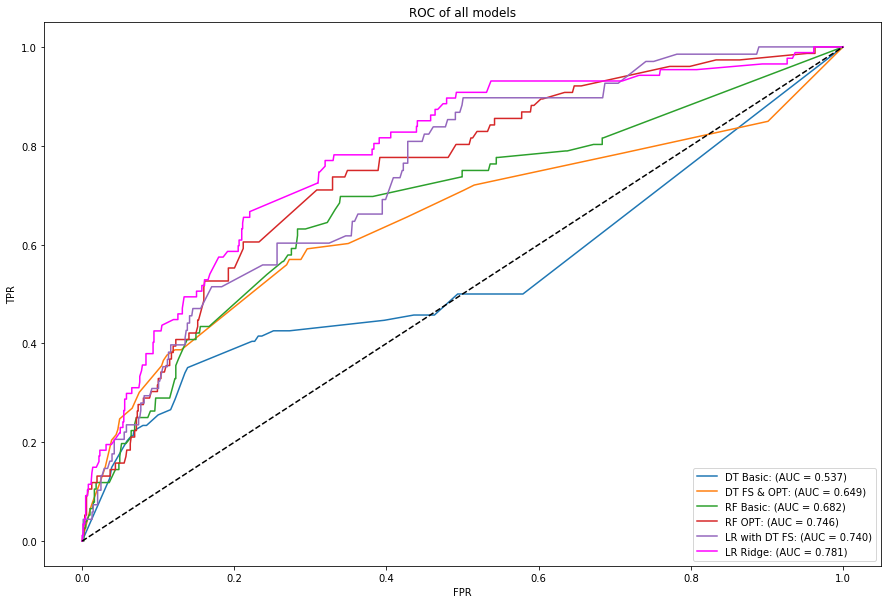
Food Happens in Vegas: How Can Restaurants Improve Their Yelp Profiles for Success?
Abstract
The purpose of this data mining project is to examine how restaurants can improve their Yelp profile to become more “successful” on Yelp in Las Vegas, Nevada. Differently from the traditional approaches to this dataset, our methodology defines “success” as a binary variable through an exploratory analysis of the restaurants’ review counts and ratings on Yelp. Feature variables include categories and attributes that Yelp users can use to select which restaurant to visit. For this project, we ran Decision Tree, Random Forest, and Logistic Regression to explore key features associated with “success” and obtain recommendations for restaurants to improve their Yelp profile. Final results indicate that determinants of success vary by cuisine type.
Comparison of the performance of different models
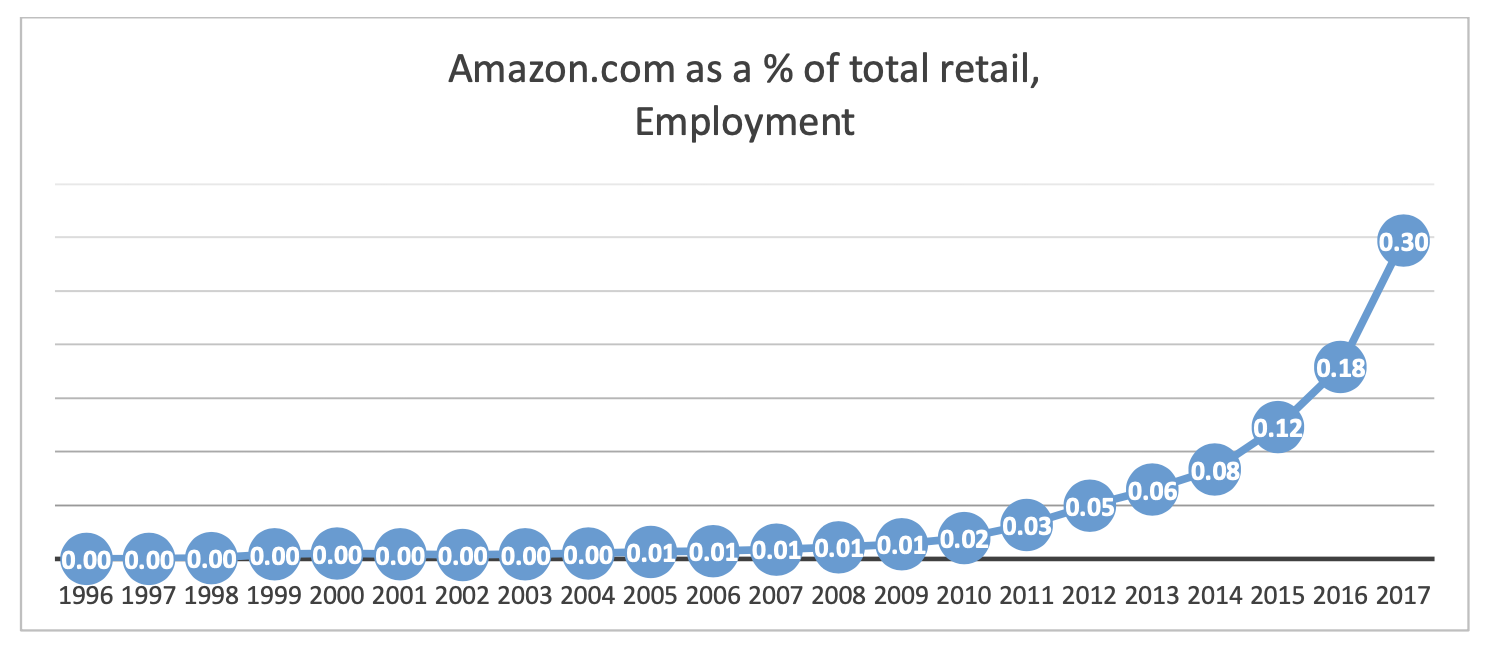
Amazon.com and Its Effect on the Retail Market and Employment
Abstract
Amazon.com is one of the fastest growing companies in the US and its expansion threatens the continuance of brick and mortar stores. As we see an increase in the number of department store shutdowns, e-commerce is seen to be at the center for blame. However, that may not be true as Amazon is becoming a large contributor in the job market by providing more positions with better wages. Additionally, other sectors including warehousing and courier services are complement industries and they might see a positive growth in employment as a result of the expansion of the e-commerce giant.
Growth in employment rate of Amazon as a percentage of total retail employment